Outils pour utilisateurs
(SS)49E HALL EFFECT SENSOR MODULES (AKA "KY-024")
(SS)49E HALL EFFECT SENSOR MODULES (AKA "KY-024")
SCHEMATICS
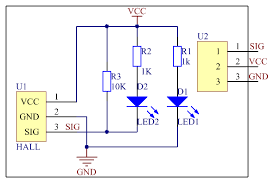
MODULE WITHOUT OPAMP
MODULE WITH OPAMP
ARDUINO WIRING
DOCUMENTATIONS
CODE
// ------------------------------------- // 49E Hall Effect Sensor - Code Example // ------------------------------------- const int pinHall = A0; void setup() { pinMode(pinHall, INPUT); Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { //we measure 10 times adn make the mean long measure = 0; for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ int value = measure += analogRead(pinHall); } measure /= 10; //voltage in mV float outputV = measure * 5000.0 / 1023; Serial.print("Output Voltaje = "); Serial.print(outputV); Serial.print(" mV "); //flux density float magneticFlux = outputV * 53.33 - 133.3; Serial.print("Magnetic Flux Density = "); Serial.print(magneticFlux); Serial.print(" mT"); delay(2000); }
/* Analog 49E Hall Effect sensor test Basic code for reading the analog output of the 49E hall effect sensor. Sensor is connected to A0, but can be any analog input pin. */ const int AnalogPin = A0; const float GAUSS_PER_STEP = 2.57; // Sensor outputs approx 1.9mV / Gauss. // ADC step is about 4.89mV / Step for 5V operation. float rawValue = 0.0; // Raw ADC Reading float gaussValue = 0.0; float zeroLevel = 518.0; // Adjust value as needed to get zero rawValue output with no magnetic field. //=============================================================================== // Initialization //=============================================================================== void setup() { pinMode (AnalogPin, INPUT); Serial.begin(9600); // Set comm speed for debug window messages } //=============================================================================== // Main //=============================================================================== void loop() { rawValue = analogRead (AnalogPin) - zeroLevel; // Output normalized to '0' with no field present Serial.print ("Reading Raw: "); Serial.println (rawValue); // Reading positive relative to the South Pole, the North Pole negative gaussValue = rawValue * GAUSS_PER_STEP; Serial.print ("Reading in Gauss: "); Serial.println (gaussValue); delay (3000); }
(31)44E HALL EFFECT SWITCH MODULE (AKA "KY-003")
SPECIFICATIONS
- Model : KY-003
- Operating Voltage : 5 VDC
- Supply Voltage, VCC : 28 V
- Reverse Battery Voltage, VRCC : -35 V
- Magnetic Flux Density, B : Unlimited
- Output OFF Voltage, VOUT : 28 V
- Reverse Output Voltage, VOUT : -0.5 V
- Continuous Output Current, IOUT : 25 mA
- Operating Temperature Range : -40°C to 85°C
- Storage Tempereture Range : -65°C to 170°C
- Length : 19mm
- Width : 15mm
FEATURES
- 4.5 V to 24 V Operation … Needs Only An Unregulated Supply
- Open-Collector 25 mA Output … Compatible with Digital Logic
- Reverse Battery Protection
- Activate with Small, Commercially Available Permanent Magnets
- Solid-State Reliability
- Small Size
- Resistant to Physical Stress
DOCUMENTATION
documentation/microcontroleurs/arduino/modules/49e_hall_effect/index.txt · Dernière modification : de f1sls